Global trade dynamics are causing many countries to refocus on internal semiconductor production, resulting in a global expansion of the semiconductor industry.
The dynamics of global trade are causing many countries to refocus on internal semiconductor production. With expansion of existing fabs and the explosion of new players fueled by government funding, China is emerging onto the global semiconductor scene. As of 2022, China has eclipsed Taiwan in global sales. And, based on recent predictions by the Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA), this significant investment in growth will likely make China one of the world’s leading producers of semiconductors. This prediction raises several timely questions to consider about the global expansion of the semiconductor industry.
What is behind this surge in Chinese semiconductor production?
China is seeking internal expansion of semiconductor production due to a variety of global factors related to both political and supply chain issues. One is the emphasis on decoupling from western producers. Another is a nationwide focus on advancing semiconductor production that includes subsidies from the government, support of procurement, and other policies.
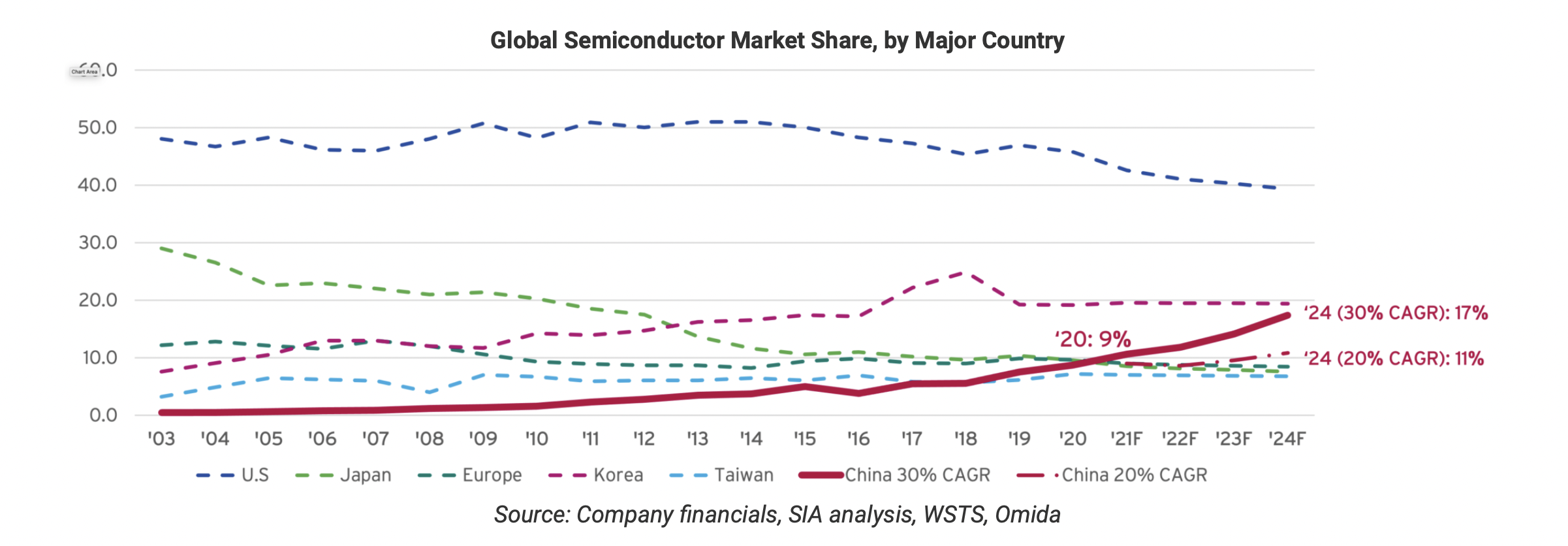
The resulting rise in Chinese chip production has increased sales from just $13 billion and only 3.8% of global chips sales in 2017, to $39.8 billion in sales and 9% of the global semiconductor market in 2020, as reported by SIA. SIA notes that this annual growth rate of 30.6% is unprecedented.
As such, China has surpassed Taiwan in sales for two years in a row and is coming up on EU and Japan, which each held 10% of the global market share in 2020. This massive, unprecedented growth reflects a significant focus of policies and investments in China’s semiconductor industry.
Where will the global expansion of the semiconductor industry lead?
SIA noted that growth was even across the Chinese semiconductor supply chain — from fabless, IDM, foundry, and OSAT. Chinese producers posted annual growth rates from 23-36%, putting them on track for domestic and perhaps even global expansion.
With such momentum, the SIA forecasts strong growth for the Chinese semiconductor industry. Assuming a steady growth rate in other countries, the SIA model predicts “the Chinese semiconductor industry could generate $116 billion in annual revenue by 2024, capturing upwards of 17.4% of global market share.” If this prediction came to pass, China would place behind only the U.S. and Korea in the global market share of semiconductor production.
Where does China lead in semiconductor production currently?
On the back end of the semiconductor production process, China ranks first in assembly, packaging, and testing in recent years, holding 38% percent of the global market share of these activities.

With the current restrictions on U.S. trade limiting new equipment purchases, China has had to pivot in other areas of semiconductor production. SIA notes that China has suspended advanced logic node manufacturing development in favor of mature fabrication technology. The result, SIA reports, is that “from September 2020 to November 2021, Chinese wafer manufacturers have added nearly 500K wafer per month (WPM) capacities in trailing nodes (>=14nm), and only an additional 10K in capacity for advanced nodes.”
What impact will this have on global semiconductor shortages?
The increase of competition from China’s rapid expansion through 2020 and beyond will likely spur U.S. and European manufacturers to expand. As a result, there will likely be an increase in demand for the supplies needed for semiconductor manufacturing.
The semiconductor supply chain remains complex and intermeshed across the globe. If the various factors supporting semiconductor production in China continue, Chinese market share will add another layer of complexity to the entire picture of global expansion of the semiconductor industry.
Read more:





